Conditional Statements in Programming | Definition, Types, Best Practices
Conditional statements in programming are used to control the flow of a program based on certain conditions. These statements allow the execution of different code blocks depending on whether a specified condition evaluates to true or false, providing a fundamental mechanism for decision-making in algorithms. In this article, we will learn about the basics of Conditional Statements along with their different types.
Table of Content
- What are Conditional Statements in Programming?
- 5 Types of Conditional Statements
- 1. If Conditional Statement:
- 2. If-Else Conditional Statement:
- 3. if-Else if Conditional Statement:
- 4. Switch Conditional Statement:
- 5. Ternary Expression Conditional Statement:
- Difference between Types of Conditional Statements in Programming:
- Difference between If Else and Switch Case
- Best Practices for Conditional Statement
- Frequently Asked Questions FAQs in Conditional Statements
What are Conditional Statements in Programming?
Conditional statements in Programming, also known as decision-making statements, allow a program to perform different actions based on whether a certain condition is true or false. They form the backbone of most programming languages, enabling the creation of complex, dynamic programs.
5 Types of Conditional Statements in Programming
Conditional statements in programming allow the execution of different pieces of code based on whether certain conditions are true or false. Here are five common types of conditional statements:
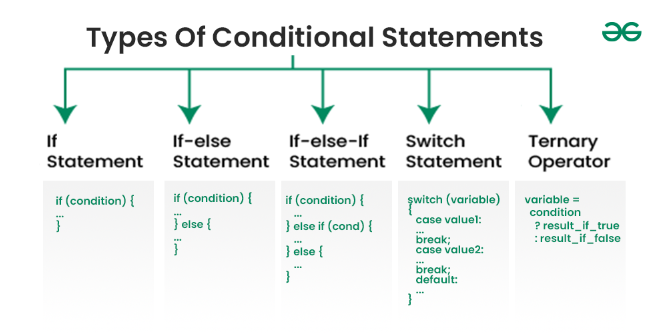
5 Types of Conditional Statements in Programming
1. If Conditional Statement:
The if statement is the most basic form of conditional statement. It checks if a condition is true. If it is, the program executes a block of code.
Syntax of If Conditional Statement:
if (condition)
// code to execute if condition is true
>
if condition is true, the if code block executes. If false, the execution moves to the next block to check.
Use Cases of If Conditional Statement:
- Checking a single condition and executing code based on its result.
- Performing actions based on user input.
Applications of If Conditional Statement:
- Validating user inputs.
- Basic decision-making in algorithms.
Advantages of If Conditional Statement:
- Simple and straightforward.
- Useful for handling basic decision logic.
Disadvantages of If Conditional Statement:
- Limited to checking only one condition at a time.
- Not suitable for complex decision-making.
Implementation of If Conditional Statement:
Java
Python
JavaScript
Output
x is positive
2. If-Else Conditional Statement:
The if-else statement extends the if statement by adding an else clause. If the condition is false, the program executes the code in the else block.
Syntax of If-Else Conditional Statement:
if (condition)
// code to execute if condition is true
> else
// code to execute if condition is false
>
if condition is true, the if code block executes. If false, the execution moves to the else block.
Use Cases of If-Else Conditional Statement:
- Executing one block of code if a condition is true and another block if it’s false.
- Handling binary decisions.
Applications of If-Else Conditional Statement:
- Error handling: For example, displaying an error message if user input is invalid.
- Program flow control: Directing program execution based on conditions.
Advantages of If-Else Conditional Statement:
- Handles binary decisions efficiently.
- Clear and concise syntax.
Disadvantages of If-Else Conditional Statement:
- Limited to binary decisions.
- May become verbose in complex scenarios.
Implementation of If-Else Conditional Statement:
Java
Python
JavaScript
Output
x is not positive
3. if-Else if Conditional Statement:
The if-else if statement allows for multiple conditions to be checked in sequence. If the if condition is false, the program checks the next else if condition, and so on.
Syntax of If-Else if Conditional Statement:
if (condition1)
// code to execute if condition1 is true
> else if (condition2)
// code to execute if condition2 is true
> else
// code to execute if all conditions are false
>
In else if statements, the conditions are checked from the top-down, if the first block returns true, the second and the third blocks will not be checked, but if the first if block returns false, the second block will be checked. This checking continues until a block returns a true outcome.
Use Cases of If-Elif-Else Conditional Statement:
- Handling multiple conditions sequentially.
- Implementing multi-way decision logic.
Applications of If-Elif-Else Conditional Statement:
- Implementing menu selection logic.
- Categorizing data based on multiple criteria.
Advantages of If-Elif-Else Conditional Statement:
- Allows handling multiple conditions in a structured manner.
- Reduces the need for nested if-else statements.
Disadvantages of If-Elif-Else Conditional Statement:
- Can become lengthy and harder to maintain with many conditions.
- The order of conditions matters; incorrect ordering can lead to unexpected behavior.
If-Else if Conditional Statement Implementation:
Java
Python
JavaScript
Output
x is not zero
4. Switch Conditional Statement:
The switch statement is used when you need to check a variable against a series of values. It’s often used as a more readable alternative to a long if-else if chain.
In switch expressions, each block is terminated by a break keyword. The statements in switch are expressed with cases.
Switch Conditional Statement Syntax:
switch (variable)
case value1:
// code to execute if variable equals value1
break;
case value2:
// code to execute if variable equals value2
break;
default:
// code to execute if variable doesn't match any value
>
Use Cases of Switch Statement:
- Selecting one of many code blocks to execute based on the value of a variable.
- Handling multiple cases efficiently.
Applications of Switch Statement:
- Processing user choices in a menu.
- Implementing state machines.
Advantages of Switch Statement:
- Provides a clean and efficient way to handle multiple cases.
- Improves code readability when dealing with many conditions.
Disadvantages of Switch Statement:
- Limited to equality comparisons, cannot use range checks or complex conditions.
- Lack of fall-through control can lead to unintentional bugs if not used carefully.
Switch Conditional Statement Implementation:
Java
JavaScript
Output
x is two
5. Ternary Expression Conditional Statement:
The ternary operator is a shorthand way of writing an if-else statement. It takes three operands: a condition, a result for when the condition is true, and a result for when the condition is false.
Syntax of Ternary Expression:
condition ? result_if_true : result_if_false
Use Cases of Ternary Expression:
- Concise conditional assignment.
- Inline conditional assignment.
Applications of Ternary Expression:
- Assigning values based on conditions in functional programming.
- Inline conditional assignment in single lines of code.
Advantages of Ternary Expression:
- Concise syntax, reducing the need for multiple lines of code.
- Suitable for simple conditional assignments.
Disadvantages of Ternary Expression:
- Can reduce code readability, especially for complex conditions or expressions.
- Limited to simple assignments; not suitable for complex branching logic.
Implementation of Ternary Expression:
Java
Python
JavaScript
Output
x is positive
Difference between Types of Conditional Statements in Programming:
| Conditional Statement | Purpose | Usage | Example |
| if | Execute code if condition is true | Single condition | if x > 5: print("x is greater than 5") |
| if-else | Execute one block if condition is true, another if false | Two mutually exclusive possibilities | if x > 5: print("x is greater than 5") else: print("x is not greater than 5") |
| if-elif-else | Execute based on multiple conditions | Multiple conditions, sequential evaluation | python if x > 5: print("x is greater than 5") elif x == 5: print("x is equal to 5") else: print("x is less than 5") |
| switch-case | Select one of many code blocks to execute based on a variable | Matching variable against multiple cases | java switch (day) |
Difference between If Else and Switch Case:
| Feature | if-else Statement | switch Statement |
| Multiple Conditions | Supports multiple conditions using else if | Supports multiple cases using case statements |
| Equality Comparison | Can handle complex conditions with relational operators | Typically checks equality with case values |
| Range Comparison | Can handle ranges using logical operators | Typically handles discrete values, not suitable for ranges |
| Fall-Through | Executes the first true condition and exits | Continues executing cases until break or end. |
| Default Case | Optional else block for default behavior | default case for unmatched values |
| Expression Type | Supports any boolean expression in the condition | Typically used with expressions resulting in discrete values |
| Readability and Maintainability | Readability may decrease with nested conditions | Readability can be maintained for multiple cases |
| Use Cases | Suitable for various conditions and complex logic | Suitable for scenarios with distinct, known values |
Best Practices for Conditional Statements in Programming:
- Keep it simple: Avoid complex conditions that are hard to understand. Break them down into simpler parts if necessary.
- Use meaningful names: Your variable and function names should make it clear what conditions you’re checking.
- Avoid deep nesting: Deeply nested conditional statements can be hard to read and understand. Consider using early returns or breaking your code into smaller functions.
- Comment your code: Explain what your conditions are checking and why. This can be especially helpful for complex conditions.
In conclusion, Conditional statements are a fundamental part of programming, allowing for dynamic and interactive programs. By understanding and using them effectively, you can create programs that are more efficient, readable, and maintainable.
Frequently Asked Questions FAQs in Conditional Statements in Programming
1. What are the 5 conditional statements?
In programming, the term “conditional statements” typically refers to constructs used to perform different actions based on whether a certain condition evaluates to true or false. The most common conditional statements are:
- If statement : Executes a block of code if a specified condition is true.
- If-else statement : Executes one block of code if the specified condition is true and another block of code if the condition is false.
- If-elif-else statement (or switch statement) : Executes different blocks of code depending on the evaluation of multiple conditions.
- Ternary operator : A concise way of writing an if-else statement that evaluates a condition and returns one of two values depending on whether the condition is true or false.
- Nested if statement : An if statement within another if statement, allowing for more complex conditional logic.
2. What are conditional statements in computer?
Conditional statements in computer programming are constructs that allow the execution of different sequences of code based on whether certain conditions are true or false. They enable programs to make decisions and choose different paths of execution dynamically. Conditional statements are crucial for controlling the flow of a program and implementing logic that responds to varying inputs or situations.
3. Why conditional statements?
Conditional statements are essential in programming for several reasons:
- Decision Making : Conditional statements allow programs to make decisions based on various conditions or inputs. They enable programs to choose different actions or paths of execution depending on the situation, making programs more flexible and adaptable.
- Control Flow : Conditional statements control the flow of execution within a program. They determine which parts of the code are executed and in what order, enabling programmers to create algorithms that respond to changing conditions or user interactions.
- Dynamic Behavior : Conditional statements enable programs to exhibit dynamic behavior by adjusting their actions based on real-time inputs or external factors. This dynamic behavior is crucial for creating interactive applications, games, and simulations.
- Error Handling : Conditional statements are often used for error handling and exception handling. Programs can use conditions to detect errors or exceptional situations and respond appropriately, such as by displaying error messages, logging errors, or taking corrective actions.
- Customization and Personalization : Conditional statements allow programs to customize their behavior based on specific criteria or user preferences. This customization enables the creation of personalized experiences in applications, websites, and other software products.
- Efficiency : Conditional statements help optimize program performance by avoiding unnecessary computations or operations. By selectively executing code based on conditions, programs can conserve resources and improve efficiency.
4. What is conditional statements in C?
In C programming, conditional statements are used to control the flow of execution based on certain conditions. There are three primary types of conditional statements in C:
- if statement : The if statement allows you to execute a block of code if a specified condition evaluates to true.
- if-else statement : The if-else statement allows you to execute one block of code if a condition is true and another block of code if the condition is false.
- if-else if-else statement : The if-else if-else statement allows you to evaluate multiple conditions sequentially and execute different blocks of code based on the first condition that evaluates to true.
- Ternary conditional operator
5. What are the conditional expressions in Python?
In Python, conditional expressions are constructs that allow you to execute different code based on whether a certain condition is true or false. The primary conditional expressions in Python include:
- if statement : The if statement allows you to execute a block of code if a specified condition evaluates to true.
- if-else statement : The if-else statement allows you to execute one block of code if a condition is true and another block of code if the condition is false.
- if-elif-else statement : The if-elif-else statement allows you to evaluate multiple conditions sequentially and execute different blocks of code based on the first condition that evaluates to true.
- Ternary conditional operator : Python also supports a ternary conditional operator ( expression if condition else expression ) which provides a concise way to write simple if-else statements.
6. What are the 4 conditional statements in Java?
In Java, like many other programming languages, you typically have four main types of conditional statements:
- if Statement : The if statement allows you to execute a block of code if a specified condition is true.
- if-else Statement : The if-else statement allows you to execute one block of code if a condition is true and another block of code if the condition is false.
- if-else if-else Statement : The if-else if-else statement allows you to evaluate multiple conditions sequentially and execute different blocks of code based on the first condition that evaluates to true.
- Switch Statement : The switch statement allows you to select one of many code blocks to be executed based on the value of a variable.



