
Here we will learn about HCF and LCM (the highest common factor and the lowest common multiple), including how to calculate the HCF and LCM of two or more numbers and recognise when to calculate the HCF or the LCM from worded problems.
There are also HCF and LCM worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
The HCF and LCM are two abbreviations for the highest common factor (HCF) and the lowest common multiple (LCM).
For example, find the HCF of 8 and 12.
Let’s start by writing the factors of 8 and 12.
Factors of > : \ 1, \ 2, \ 4, \ 8
Factors of > : \ 1, \ 2, \ 3, \ 4, \ 6, \ 12
There are several numbers that occur in both lists (1, \ 2, and 4).
The highest positive integer that occurs in each list is 4, and so the highest common factor of 8 and 12 is 4.
For example, find the LCM of 8 and 12.
Let’s start by writing the first 12 multiples of 8 and 12.
Multiples of > : \ 8, \ 16, \ 24, \ 32, \ 40, \ 48, \ 56, \ 64, \ 72, \ 80, \ 88, \ 96
Multiples of > : \ 12, \ 24, \ 36, \ 48, \ 60, \ 72, \ 84, \ 96, \ 108, \ 120, \ 132, \ 144

To calculate the HCF or LCM of two or more numbers, we can write out a list of factors or multiples as we have above, however this approach can be very time consuming and can be complicated when dealing with factors and multiples of large numbers ( 3 digit numbers in particular).
We can therefore utilise prime factors to calculate these values.
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic states that every positive integer is either a prime number, or can be written as a product of its prime factors. Every number has a unique set of prime factors.
By presenting prime factors within a Venn diagram, we can quickly determine both the HCF and LCM of the two or more numbers in the question.
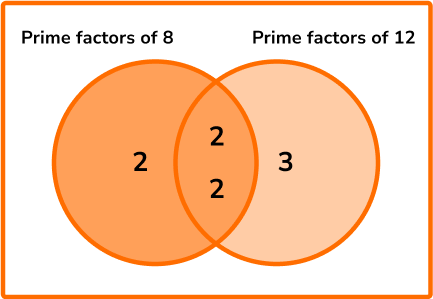
The intersection of the two circles contains the highest common factor where we multiply the values within the intersection together.
Here, the HCF of 8 and 12 is equal to 2\times=4.
The union of the two circles contains the lowest common multiple where we multiply the values within both circles together.
Here, the LCM of 8 and 12 is equal to 2\times(2\times)\times=24.
Notice that the values for the HCF and LCM match those values previously mentioned using the alternative method.
Furthermore, as the lowest common multiple is calculated by multiplying all of the factors together within the Venn diagram, the lowest common multiple can be found by multiplying the highest common factor by the remaining prime factors.
\text = \text < HCF >\times \text
This allows us to solve problems where we are given the HCF and LCM of two numbers and we need to determine the original two numbers.
In order to calculate the highest common factor of two or more numbers:
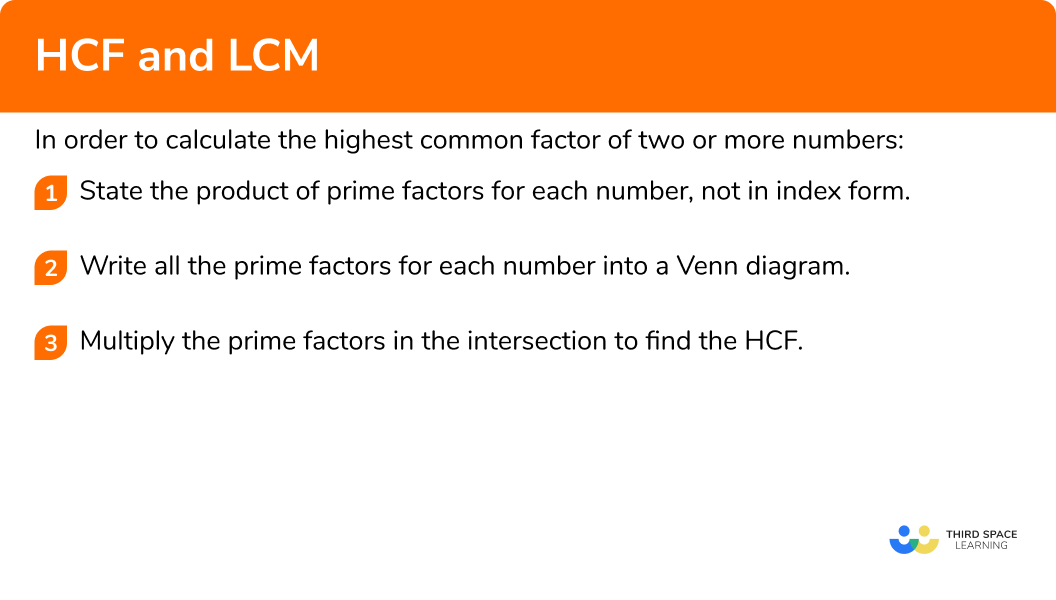
In order to calculate the lowest common multiple of two or more numbers:



Get your free hcf and lcm worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.


Get your free hcf and lcm worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
HCF and LCM is part of our series of lessons to support revision on factors, multiples and primes. You may find it helpful to start with the main factors, multiples and primes lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include: